As enterprises move toward Kubernetes, Microservices , and cloud platforms, extending Alfresco Content Services (ACS) has shifted from traditional AMP/JAR customisations to modern, cloud-native Spring Boot extensions.This new approach is lightweight, scalable, easier to maintain, and aligns perfectly with today’s DevOps practices.
Why Build Cloud-Native Extensions?
Traditionally, developers extended Alfresco by deploying AMP modules inside the repository server.
This tightly coupled model had limitations:
- Difficult to scale independently
- Deployments required restarting the Alfresco server
- Hard to test and maintain
- Not ideal for cloud/Kubernetes environments
Cloud-native extensions solve all of this.
You build an external microservice using Spring Boot and interact with Alfresco purely through REST APIs, keeping Alfresco clean, stable, and scalable.
Architecture Overview
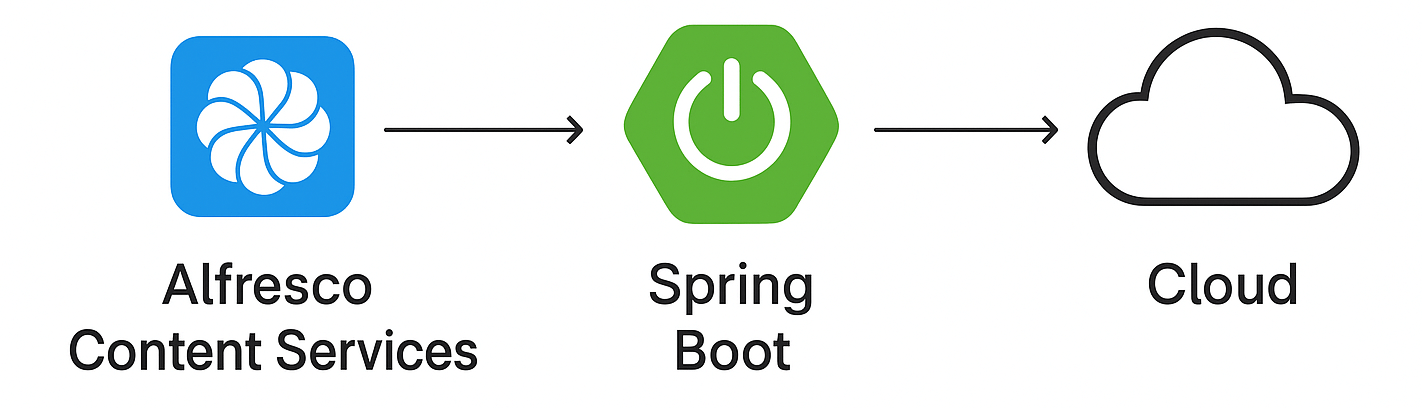
A Spring Boot microservice connects to Alfresco via REST APIs, processes events or scheduled jobs, and updates content or metadata in cloud platforms such as Google Drive, OneDrive, or SharePoint.
Key Components in the Architecture
1.API Layer :
Handles inbound/outbound communication with Alfresco and external systems.
2.Processing Layer :
Executes business logic such as metadata transformations, file synchronization, validations, and AI-based processing.
3.Scheduler / Job Engine :
Runs periodic tasks such as:
- Daily sync jobs
- Cleanup operations
- Metadata refresh
- Report generation
4.Event Listener :
Responds to real-time triggers from Alfresco or external applications.
What Can You Build with Cloud-Native Extensions?
1.Document Synchronization :
Automatically sync documents between Alfresco and cloud storage:
- Google Drive
- Microsoft OneDrive
- SharePoint Online
- Dropbox
- Box
Use cases:
- Enterprise file sharing
- Backup and archiving
- Bi-directional collaboration
2.Metadata Automation :
The microservice can:
- Fetch data from an external database or ERP
- Derive metadata using AI/ML
- Apply aspects and properties inside Alfresco
Examples:
- Auto-classify documents
- Apply retention policies
- Update workflow-related metadata
3.Workflow Integrations :
Trigger or update APS/Activiti workflows externally.
Examples:
- Kick off a HR onboarding workflow when data comes from Workday
- Start an approval workflow when files are uploaded to Drive
- Automate business processes based on external triggers
4.Event-Driven Integrations :
Instead of polling, the service can respond to events using:
- Alfresco AIMS (Alfresco Insight Engine)
- Webhooks from external systems
- Custom event emitters
Possible automations:
- Notify Microsoft Teams when a file is uploaded
- Execute OCR on new PDFs
- Auto-tag documents
Benefits of This Approach
1.Zero impact on Alfresco core :
- No AMP deployment
- No downtime
- No risk of breaking repository stability
2.Cloud-ready :
Runs on:
- Kubernetes
- Docker
- AWS ECS / Azure AKS
- On-premise VM
3.Automatic Scaling and High Availability
While Docker provides containerization, Kubernetes takes it to the next level by offering powerful orchestration features.
When your Alfresco integration runs as a Kubernetes microservice, you get:
- Auto-scaling (HPA) based on CPU, memory, queue size, or custom metrics
- Self-healing — automatic restart of failed pods
- Rolling updates with zero downtime
- Blue–green and canary deployments for safe releases
- Automated service discovery and load balancing
- Resource governance (limits/requests to prevent overload)
This ensures your Alfresco extension remains highly available, fault-tolerant, and resilient, even during heavy sync jobs, metadata processing, or large migrations.
When Should You Build Cloud-Native Extensions?
Use Spring Boot microservices when:
- You need heavy processing (large sync tasks, metadata extraction)
- You’re integrating with multiple external systems
- Alfresco should not be overloaded
- You want scalable, container-based deployment
- You want fully automated maintenance jobs
Conclusion
Cloud-native extensions represent the future of Alfresco development.
Using Spring Boot + REST APIs, developers can build:
- Scalable
- Testable
- Maintainable
- Cloud-ready
extensions without modifying the Alfresco core.